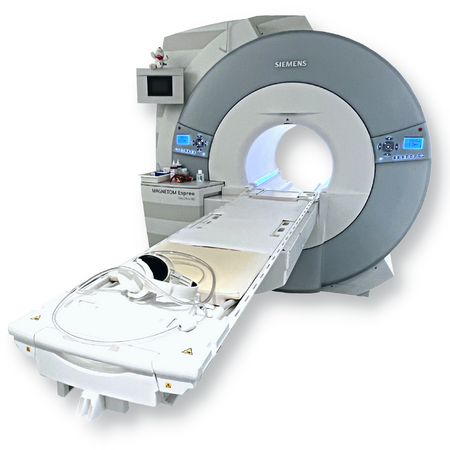
MRI Machine in Rajasthan

Magnetic resonance imaging is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machine is a medical imaging device used to create detailed images of the inside of the body without using harmful radiation. Instead, it uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and computer technology to produce high-resolution cross-sectional images of organs, tissues, and skeletal structures. The MRI machine typically looks like a large cylindrical tube surrounded by a circular magnet. The patient lies on a motorized bed that slides into the scanner. When inside, the strong magnetic field aligns the hydrogen atoms in the body, and radiofrequency waves then manipulate these atoms. As they return to their normal state, they emit signals, which the computer converts into images. MRI is widely used for diagnosing conditions related to the brain, spinal cord, joints, heart, blood vessels, and internal organs, offering excellent soft-tissue contrast compared to X-rays or CT scans.
- High-Resolution Imaging–Provides highly detailed images of soft tissues, organs, and skeletal structures.
- Non-Invasive & Radiation-Free–Uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves instead of ionizing radiation (safe for repeated use).
- Multiple Imaging Modes–Supports T1, T2, FLAIR, Diffusion, Perfusion, and Functional MRI (fMRI) scans.
- Advanced Magnet Technology–Usually uses superconducting magnets (1.5T, 3T, or higher) for stronger signals and better clarity.
- 3D & Multi-Planar Imaging–Captures cross-sectional, sagittal, coronal, and 3D reconstructed views.
- Functional Imaging–MRI measures brain activity by detecting blood flow changes.
- Contrast Imaging Capability–Can use contrast agents (like gadolinium) for enhanced visualization of abnormalities.
- Noise Reduction Features–Modern systems include quieter scanning modes and patient comfort enhancements.
- Wide Bore Designs–Newer machines have larger openings (70 cm or more) to reduce claustrophobia and accommodate all body types.
- Real-Time Monitoring–Some models offer live imaging for interventional procedures.
- Digital Data Storage & Sharing–Images can be stored, transferred, and integrated with PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System).
- Specialized Coils–Various surface and body coils are used for high-quality imaging of specific regions (brain, spine, knee, cardiac, etc.).